Banks in Japan
This guide provides essential information for navigating the banking system in Japan, ensuring you can effectively manage your finances while living in the country.

Understanding how banks operate in Japan is essential for managing your finances effectively while living in the country. Whether you're planning to stay short-term or long-term, opening a bank account and utilizing banking services can greatly enhance your experience in Japan. Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate the banking system in Japan.
Types of Banks in Japan
Japan has various types of banks, each serving different needs:
- Major Banks: These include well-known institutions like Mitsubishi UFJ (MUFG), Mizuho, and Sumitomo Mitsui (SMBC). They offer comprehensive banking services and have branches nationwide.
- Regional Banks: These banks operate primarily within specific prefectures or regions, providing localized services.
- Online Banks: Banks such as Sony Bank and Rakuten Bank offer convenient online banking services with lower fees and better interest rates.
- Post Office Banks: Japan Post Bank (Yucho) provides banking services at post offices across the country, making it accessible and convenient.
Opening a Bank Account
To open a bank account in Japan, you will need the following documents:
- Residence Card: Proof of your legal status in Japan.
- Passport: Identification purposes.
- Personal Seal (Hanko): Some banks require a personal seal for official documents.
- Proof of Address: Utility bill or rental agreement.
- Phone Number: Contact information.
The process typically involves filling out an application form and providing the necessary documentation. Some banks may have English-speaking staff or provide forms in English to assist foreigners.
Types of Accounts
- Ordinary Account (Futsu Yokin): Standard savings account used for daily transactions, salary deposits, and bill payments.
- Fixed Deposit Account (Teiki Yokin): Savings account with higher interest rates for fixed-term deposits.
- Foreign Currency Account: Allows you to hold and transact in foreign currencies.
Banking Services
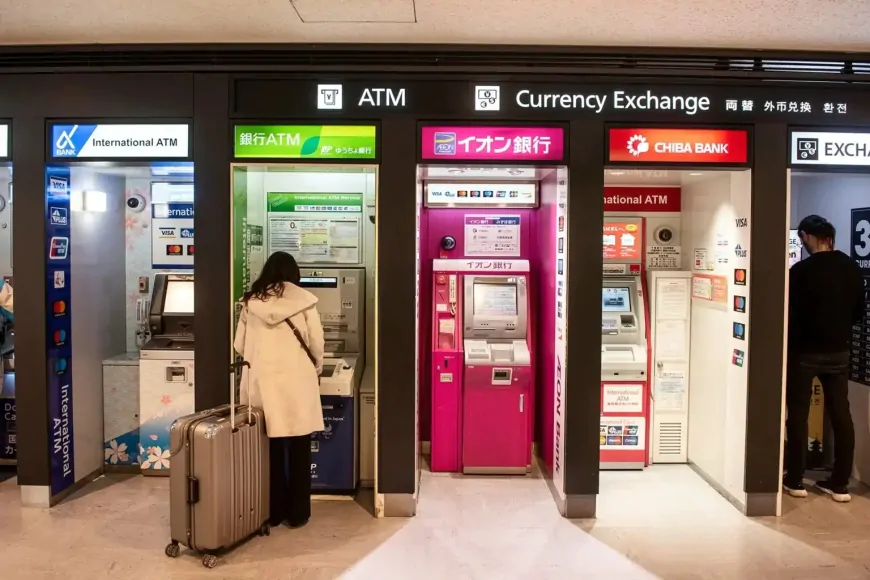
- ATM Services: ATMs are widely available, with many offering English language options. Japan Post Bank and Seven Bank ATMs are convenient for foreigners due to their widespread locations and English interfaces.
- Online Banking: Most banks offer online banking services, allowing you to manage your account, transfer money, and pay bills online. Some banks have English-language online banking platforms.
- Credit and Debit Cards: Credit cards can be difficult for foreigners to obtain initially, but debit cards are readily available. Prepaid cards and e-money cards like Suica and Pasmo are also popular.
- International Money Transfers: Services like Western Union and TransferWise are available for transferring money overseas. Major banks also offer international wire transfers.
Bank Fees
Bank fees in Japan can vary widely. Common fees include:
- ATM Withdrawal Fees: Fees may apply when using ATMs outside of business hours or using different bank ATMs.
- Transfer Fees: Domestic and international transfer fees.
- Account Maintenance Fees: Some banks may charge a fee for maintaining certain types of accounts.
Tips for Foreigners
- Choose the Right Bank: Consider your needs and choose a bank that offers the services and convenience you require. Online banks are often a good option for lower fees and easy access.
- Learn Basic Japanese Banking Terms: Knowing basic terms can be helpful when dealing with bank staff and services.
- Use International Services: If you need to transfer money abroad frequently, consider using international money transfer services for better rates and convenience.
Banking in Japan can be straightforward with the right information and preparation. By understanding the types of banks, account options, and available services, you can manage your finances effectively and make the most of your time in Japan. Whether you choose a major bank, regional bank, or online bank, the key is to find the one that best fits your needs.
記事に関連する商品